Disclaimer: This information is based on publicly available data and market research and may not be fully accurate; all quotes and recommendations should be independently verified with vendors.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is often perceived as a complex technology because it requires the integration of both physical components (tags, readers, antennas) and software systems (data capture, processing, analytics). On top of this, RFID’s value can be highly context-dependent – its benefits vary widely across industries, making use cases seem ambiguous or overlapping.
This white paper aims to simplify the conversation by examining commercially available RFID solutions, how they are positioned in the market, and what factors influence successful deployment. Rather than focusing solely on technical specifications, this document connects RFID technology to practical business applications and outlines decision points that determine adoption success.
Historically, RFID has found strong adoption in industries such as Retail, Healthcare, Logistics, Automotive, and Manufacturing, among others. Common use cases include:
- Product Authentication – Unique product identification to protect brand integrity and ensure quality assurance.
- Inventory Tracking – Rapid detection and tracking of inventory units, enabling efficient, real-time, and highly accurate inventory positions.
- Asset Management – Locating and tracking high-value equipment, tools, or returnable containers to reduce loss and downtime.
- Supply Chain Visibility – Enabling real-time tracking from origin to end-customer for improved logistics planning.
- Compliance & Safety Monitoring – Tracking pharmaceuticals, medical devices, or regulated products to meet industry-specific compliance requirements.
- Customer Experience Enhancements – Supporting applications like self-checkout, interactive displays, and smart fitting rooms in retail environments.
- Process Automation – Automating manufacturing workflows, vehicle tracking in yards, and tool allocation in production environments.
While RFID technology is broad, most deployments consist of three fundamental components:
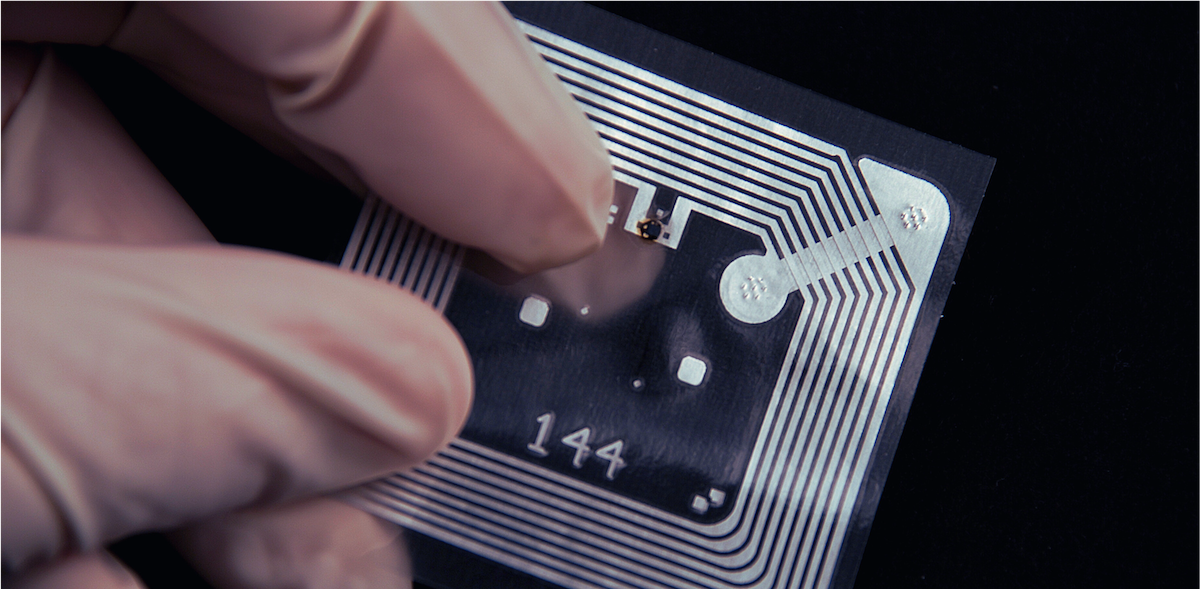
- Tags – The identifiers attached to products, assets, or containers, carrying encoded information that can be read wirelessly. Tags may be passive (powered by the reader signal) or active (self-powered). They vary in form factors, durability, and memory capacity.
- Hardware – The physical equipment required to read and process tag data, including fixed or handheld readers, antennas, and in some cases, specialized portals or conveyor-mounted systems.
- Software – The digital layer that captures, processes, and integrates RFID read events into business systems. This includes middleware for filtering and interpreting tag reads, as well as analytics and integration into ERP, WMS, or POS platforms.
Tags
RFID tag pricing can range from $0.02 to over $0.30 USD for common passive tags (no onboard power), while specialized active tags (self-powered, longer range) can range from $5 to over $100 USD depending on capabilities. The choice of tag directly impacts system performance and total cost of ownership.
Tag price is influenced by quality, form factor, durability, and specialized features. While low-cost tags—often from overseas suppliers—can be tempting, they may introduce risks such as inconsistent quality, reduced read range, or performance issues under certain environmental conditions. For that reason, these vendors have not been considered in this analysis. Savings may be possible, but extensive testing is strongly recommended before committing to large-scale purchases, particularly for mission-critical deployments.
Key considerations when selecting an RFID tag provider:
- Tag Size – Impacts read range, application method, and compatibility with the tagged item.
- Tag Type – Passive or Active, Label or Hard Tag, Standard or Ruggedized.
- Read Range – Varies based on antenna design, power, and environmental factors.
- Features & Customization – Durability (waterproof, heat-resistant), attachment methods (adhesive, screw-mount, embedded), and printing/encoding requirements.
- Product Interaction – Material type (metal, liquid, cardboard, plastic), packaging design, and dimensions all affect performance.
| Vendor | Tag Type Supported | Service Bureau | Rugged Production | Inlay Manufacturing | Frequencies | Chip Manufacturer | Industry | Global Availability | Cost Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avery Dennison | Inlays, Labels | Yes | No | Yes (Limited) | UHF | Impinj | Retail, Logistics, Healthcare, Automotive, Aviation | Global | Moderate | RFID leader in consumer market industries |
| Checkpoint | Inlays, Labels, Hard Tags | Yes | Yes | Yes (Limited) | UHF | Impinj | Retail, Logistics, Manufacturing, Aviation | Global | Moderate | Vertically integrated provider from inlay to label to tagging services |
| Sensormatic | Labels, Hard Tags | Yes | Yes | Yes (Outsourced) | UHF | Impinj | Retail | Global | Moderate | End to end RFID combined with loss prevention/EAS systems |
| SML | Inlays, Labels | Yes | No | Yes (Limited) | UHF | Impinj, NXP | Retail, F&B, Healthcare, Aviation, Agriculture | Global | Moderate | Leading cloud RFID platform, strong fashion retail presence |
| HID Global | Labels, Embedded Tags, Hard Tags | No | Yes | Yes | HF, UHF, LF, NFC | HID, Impinj | Retail, Logistics, Industrial, Laundry, Healthcare, Automotive, Agriculture | Global | High | Broadest form factor range, including rugged and specialty tags |
| Tageos | Inlays, Labels, Sensor Inlays | No | Yes | Yes (Limited) | UHF, HF, NFC | NXP, Asygn | Retail, Supply Chain, F&B, Industrial | North America, EMEA, APAC | Moderate | One of the top inlay producers, sustainable paper-based tags |
| Xerafy | Hard Tags | Yes | Yes | Yes (Limited) | UHF | Impinj | Manufacturing, Logistics, Healthcare | Global | High | Renowned for rugged, long-range, high-temp metal tags |
| PulpaTronics | Paper-Based Chipless Tags | No | Yes (sustainable format) | Yes (laser on paper) | Paper Antenna (RFID Alternative) | Not Applicable | Retail, Logistics | North America | Low | Innovative chipless, recyclable tags – ecofriendly approach |
| Beontag | Inlays, Labels, Hard Tags | No | Yes | Yes (Limited) | UHF, NFC | Impinj | Retail, Logistics, Automotive | Global | Moderate | Sustainable print, dual-frequency options |
| Turck | Hard Tags | No | Yes | Yes (Limited) | UHF, HF, LF | Impinj, NXP | Manufacturing, Automotive, Industrial | Global | High | Strong focus on automation integration in harsh industries |
Disclosure: This information is an aggregate of Ready experience, market research material, and publicly available data. Inaccurate or out-of-date information may be included, and we advise you to contact these organizations directly for further information.
About Ready
Ready is a consulting agency committed to providing innovative solutions to address operational and technological needs. With a focus on strategy, automation, and enablement, Ready specializes in offering forward-looking solutions for the modern customer. With operations in the United States, Philippines, Australia, and Thailand, and plans to expand further, Ready is set to become a global force in the consulting world.
Share

